
The Ultimate Guide to User Experience (UX): How to Enhance User Satisfaction and Engagement
- Product Design /
As businesses compete for attention in a crowded online marketplace, the quality of their digital products’ User Experience (UX) can make or break their success. A seamless, intuitive, and enjoyable user experience not only attracts users but also keeps them coming back, ultimately driving growth and profitability.
User Experience encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a product, service, or company. It goes beyond the mere functionality of a website or application, focusing on the emotional and perceptual impact of the interaction. By prioritizing UX, businesses can create digital products that not only meet users’ needs but also exceed their expectations, fostering lasting relationships and brand loyalty.
Throughout this article, you’ll gain insights into the UX design process, from research and analysis to design, testing, and implementation. We’ll also discuss best practices for creating excellent user experiences and highlight the numerous benefits of investing in UX, including increased user satisfaction, higher conversion rates, and reduced development costs.
Whether you’re a designer, developer, marketer, or business owner, understanding the power and potential of User Experience is essential for success. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to create exceptional digital products that captivate users and drive meaningful results. So, let’s embark on this journey to unlocking the secrets of User Experience and transforming the way users interact with your digital products.
What is User Experience?
User Experience (UX) is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on the overall experience a user has when interacting with a product, service, or company. It encompasses all aspects of the user’s journey, from their initial awareness and discovery of the product to their ongoing engagement and loyalty. The goal of UX design is to create products that are not only functional and usable but also enjoyable, memorable, and valuable to the user.
At its core, User Experience is about understanding and empathizing with users’ needs, preferences, and behaviors. It involves researching and analyzing target audiences to gain insights into their motivations, pain points, and goals. By placing the user at the center of the design process, UX professionals aim to create solutions that are tailored to the user’s context and expectations.
UX design goes beyond the visual aesthetics of a product, although that is certainly an essential component. It also considers factors such as usability, accessibility, performance, and emotional resonance. A well-designed user experience is intuitive, efficient, and satisfying, enabling users to accomplish their tasks with minimal friction and maximum delight.
Some key aspects of User Experience include:
- Usability: The ease with which users can navigate and interact with a product to achieve their goals.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that the product is usable by people with diverse abilities and disabilities.
- Desirability: Creating a product that is visually appealing, engaging, and emotionally resonant.
- Findability: Enabling users to easily discover the information or features they need within the product.
- Credibility: Establishing trust and credibility through a professional, reliable, and secure user experience.
By addressing these various facets of the user’s experience, UX designers create products that not only meet functional requirements but also foster positive emotions, build brand loyalty, and drive user engagement. A well-crafted UX created by a UX Agency can differentiate a product from its competitors, increase customer satisfaction, and ultimately contribute to the success of the business.
The 5 Elements of User Experience
To create a successful and memorable User Experience, designers must consider various aspects of the user’s interaction with the product. Jesse James Garrett, in his book The Elements of User Experience, proposed a framework that breaks down User Experience into five essential elements. These elements, often referred to as the “5 Planes of UX,” include Strategy, Scope, Structure, Skeleton, and Surface. Let’s explore each of these elements in detail.
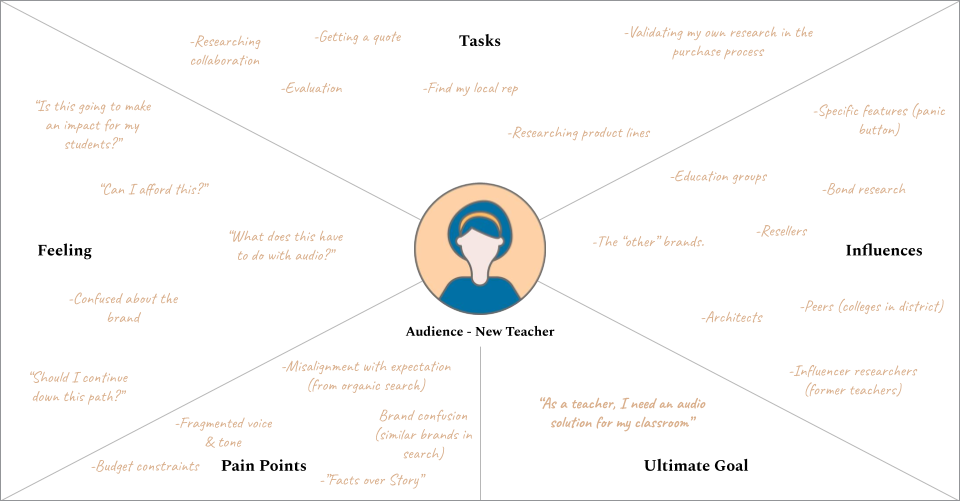
1. Strategy
The foundation of any successful UX design lies in a well-defined strategy. This element involves understanding the business goals and user needs, and aligning them to create a product that meets both. Key activities in the strategy phase include:
- User research: Conducting surveys, interviews, and observations to gain insights into user behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
- Persona development: Creating fictional representations of target users based on research data to guide design decisions.
- Defining project goals: Establishing clear objectives for the product, such as increasing user engagement or improving conversion rates.
2. Scope
Once the strategy is in place, the next step is to define the scope of the product. This element involves determining the features and functionality that will be included in the product, as well as the content requirements. Key activities in the scope phase include:
- Feature prioritization: Identifying and prioritizing the most important features based on user needs and business goals.
- Content inventory: Cataloging and auditing existing content to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
- Requirements gathering: Documenting the functional and content requirements for the product.
3. Structure
The structure element focuses on organizing the content and functionality of the product in a logical and intuitive manner. It involves creating a clear information architecture and designing the user flow. Key activities in the structure phase include:
- Information architecture: Organizing and labeling content in a way that is easy for users to navigate and understand.
- Interaction design: Defining how users will interact with the product, such as through buttons, menus, or gestures.
- User flow: Mapping out the journey map of the steps users will take to complete tasks and achieve their goals within the product.
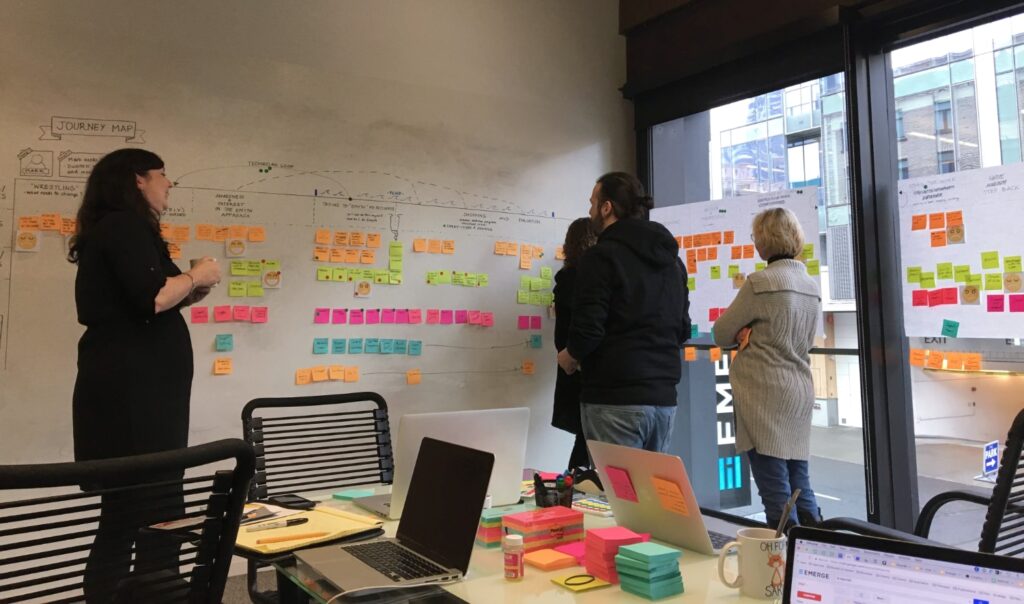

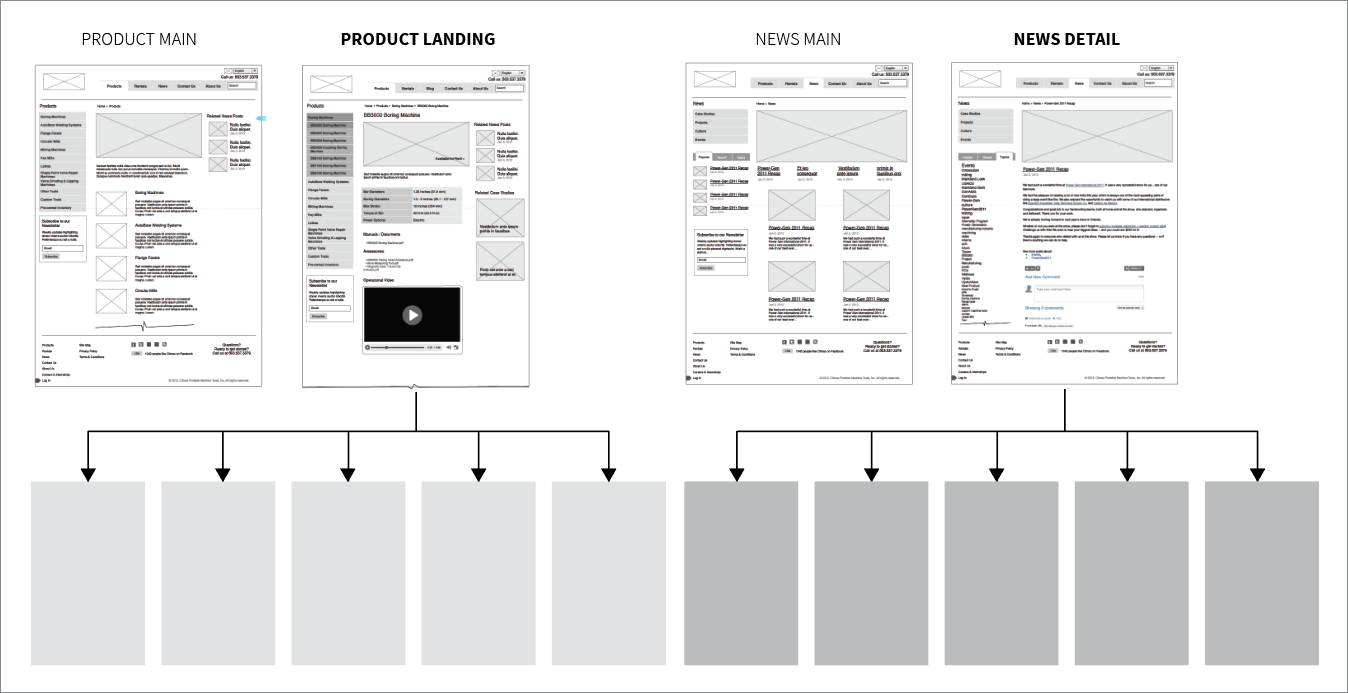
4. Skeleton
The skeleton element deals with the placement and arrangement of interface elements on the screen. It involves creating wireframes and prototypes that define the layout and navigation of the product. Key activities in the skeleton phase include:
- Interface design: Designing the visual layout of the product, including the placement of buttons, forms, and content.
- Navigation design: Creating a clear and intuitive navigation system that helps users find what they need quickly and easily.
- Wireframing: Creating low-fidelity sketches or diagrams that outline the basic structure and layout of the product.
- Prototyping: Building interactive models of the product to test and refine the design.
5. Surface
The surface element is the final plane of UX design, focusing on the visual treatment of the product. It involves creating a cohesive and engaging visual design that aligns with the brand and enhances the user experience. Key activities in the surface phase include:
- Visual design: Designing the typography, color scheme, and imagery of the product to create a consistent and appealing visual language.
- Branding: Incorporating the company’s brand identity and values into the visual design of the product.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that the visual design is accessible to users with diverse abilities and disabilities.
- Responsive design: Optimizing the visual design for various screen sizes and devices to provide a seamless experience across platforms.
By addressing each of these five elements throughout the UX design process, designers can create products that are not only functional and usable but also engaging, memorable, and valuable to users.
The UX Design Process
Creating a successful user experience involves a systematic and iterative process that encompasses research, design, testing, and implementation. While the specific steps may vary depending on the project and the team, the UX design process generally follows a similar pattern. Let’s explore the key phases of the UX design process.
1. Research and Analysis
The first step in the UX design process is to gather insights into the users, their needs, and the business goals. This phase involves various research methods, such as:
- User interviews: Conducting one-on-one interviews with target users to understand their behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
- Surveys: Distributing online questionnaires to gather quantitative data about user attitudes and opinions.
- Competitor analysis: Examining the user experience of competing products to identify opportunities for differentiation and improvement.
- Analytics review: Analyzing data from existing products or services to identify usage patterns and areas for optimization.
The insights gathered during the research phase inform the subsequent stages of the design process and help ensure that the final product meets the needs of both users and the business.
2. Design and Prototyping
Armed with a deep understanding of the users and their needs, the next step is to translate those insights into tangible design solutions. This phase involves various design activities, such as:
- Information architecture: Organizing the content and functionality of the product in a logical and intuitive manner.
- Wireframing: Creating low-fidelity sketches or diagrams that outline the basic structure and layout of the product.
- Prototyping: Building interactive models of the product to test and refine the design.
- Visual design: Developing the typography, color scheme, and imagery of the product to create a cohesive and engaging visual language.
Throughout the design phase, it’s essential to collaborate closely with stakeholders and incorporate their feedback to ensure that the design aligns with the project goals and user needs.
3. Testing and Iteration
Once the design has been developed, it’s crucial to test it with real users to validate its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This phase involves various testing methods, such as:
- Usability testing: Observing users as they interact with the product to identify usability issues and opportunities for optimization.
- A/B testing: Comparing two or more design variations to determine which one performs better in terms of user engagement and conversion.
- User feedback: Gathering qualitative feedback from users through surveys, interviews, or feedback forms.
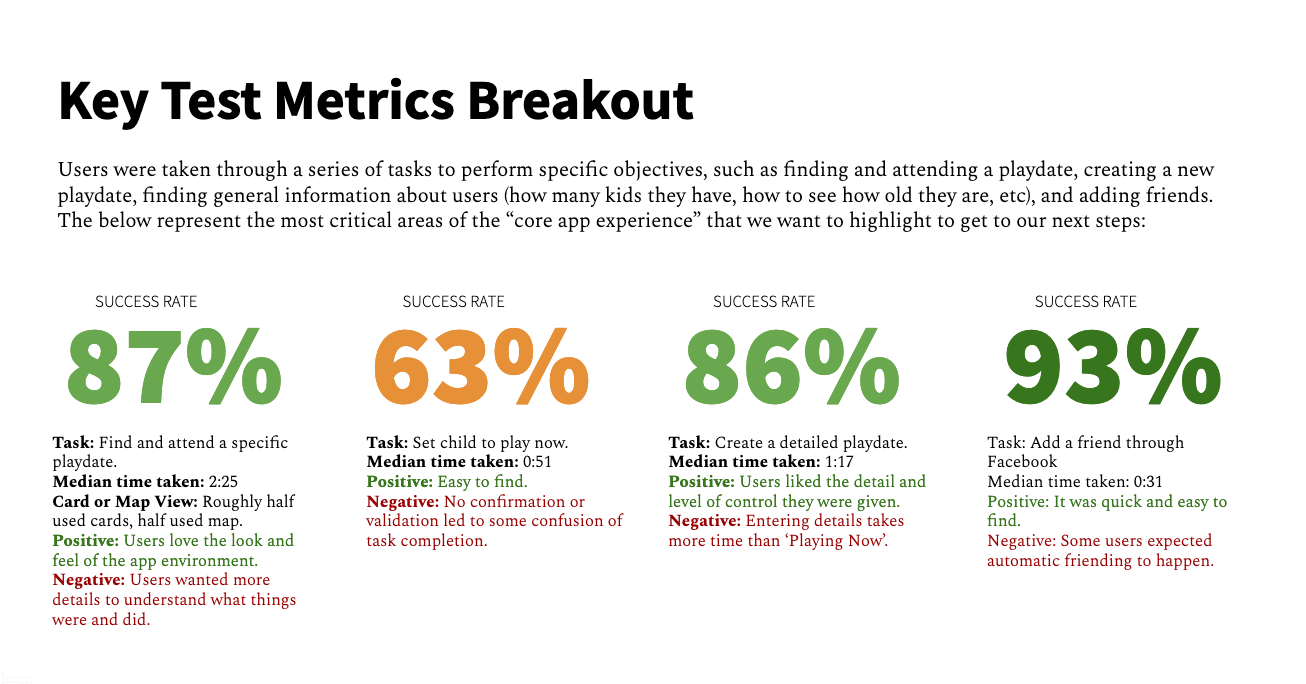
Based on the insights gathered during testing, the design is refined and iterated upon until it meets the desired level of usability and user satisfaction.
4. Implementation and Launch
Once the design has been finalized and tested, it’s time to implement it and launch the product. This phase involves various technical and project management activities, such as:
- Development: Building the product based on the final design specifications.
- Quality assurance: Testing the product to ensure that it meets the required quality standards and is free of bugs or errors.
- Launch planning: Developing a strategy for launching the product, including marketing, user onboarding, and customer support.
After the product has been launched, it’s essential to continue monitoring its performance and gathering user feedback to identify opportunities for ongoing optimization and improvement.
By following this iterative and user-centered design process, UX designers can create products that not only meet the needs of users but also drive business success.
Best Practices for Creating Excellent User Experiences
Creating an exceptional user experience requires a combination of empathy, creativity, and adherence to proven design principles. By following best practices, UX designers can craft digital products that are intuitive, engaging, and memorable. Here are some key best practices for creating excellent user experiences.
1. Understand Your Target Audience
The foundation of any successful UX design lies in a deep understanding of the target users. Conducting thorough user research, creating detailed user personas, and empathizing with users’ needs, goals, and pain points are essential for designing solutions that resonate with them. By keeping the user at the center of the design process, UX designers can create products that are tailored to their specific context and expectations.

2. Focus on Usability and Accessibility
A great user experience is one that enables users to accomplish their tasks easily and efficiently, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. Designers should prioritize usability by creating clear and intuitive navigation, providing helpful feedback and guidance, and minimizing cognitive load. Accessibility should also be a key consideration, ensuring that the product is usable by people with diverse abilities, such as those with visual, auditory, or motor impairments.
3. Ensure Consistency and Clarity
Consistency is a crucial aspect of creating a seamless and intuitive user experience. Designers should use consistent design patterns, terminology, and interactions throughout the product to help users develop a mental model and navigate the interface with ease. Clear and concise language, well-organized content, and visual hierarchy are also essential for guiding users and reducing confusion.
4. Design for Emotional Engagement
By embracing the principles of Human Centered Design, designers can create user experiences that go beyond mere functionality and usability. Human Centered Design focuses on understanding and addressing the emotional needs of users, enabling designers to craft interactions that evoke positive emotions and create memorable, delightful experiences. This can be achieved by incorporating engaging visuals, animations, and micro-interactions that surprise and delight users.
Human Centered Design also emphasizes the importance of personalization and customization options, which help create a sense of ownership and emotional connection with the product, ultimately leading to a more meaningful and satisfying user experience.
5. Optimize for Performance and Speed
Users expect products to be fast, responsive, and reliable. Designers should optimize the product’s performance by minimizing page load times, reducing the number of steps required to complete tasks, and providing clear feedback on system status. A product that performs well not only enhances the user experience but also improves user satisfaction and retention.
6. Incorporate User Feedback and Analytics
Creating an excellent user experience is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning and improvement. Designers should actively seek user feedback through surveys, interviews, and usability testing and use that insight to iterate and refine the product. Analyzing user behavior and interaction data through embedded analytics tools can also provide valuable insights into how users engage with the product and identify areas for optimization.
7. Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams
Creating a great user experience is a collaborative effort that involves various stakeholders, including designers, developers, product managers, and marketers. Effective collaboration and communication among cross-functional teams are essential for ensuring that the product meets both user needs and business goals. Regular design reviews, feedback sessions, and iteration cycles can help align the team and create a shared vision for the product.
By following these best practices and continually iterating based on user feedback and data, UX designers can create digital products that are not only functional and usable but also emotionally engaging and memorable.
The Difference Between UI and UX
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) are two closely related but distinct aspects of the product design process. While they are often used interchangeably, understanding the difference between UI and UX is crucial for creating successful digital products.
User Interface (UI) refers to the visual and interactive elements of a product, such as buttons, menus, forms, and typography. It is the tangible part of the product that users see and interact with. The goal of UI design is to create an aesthetically pleasing, intuitive, and efficient interface that enables users to navigate and engage with the product seamlessly.
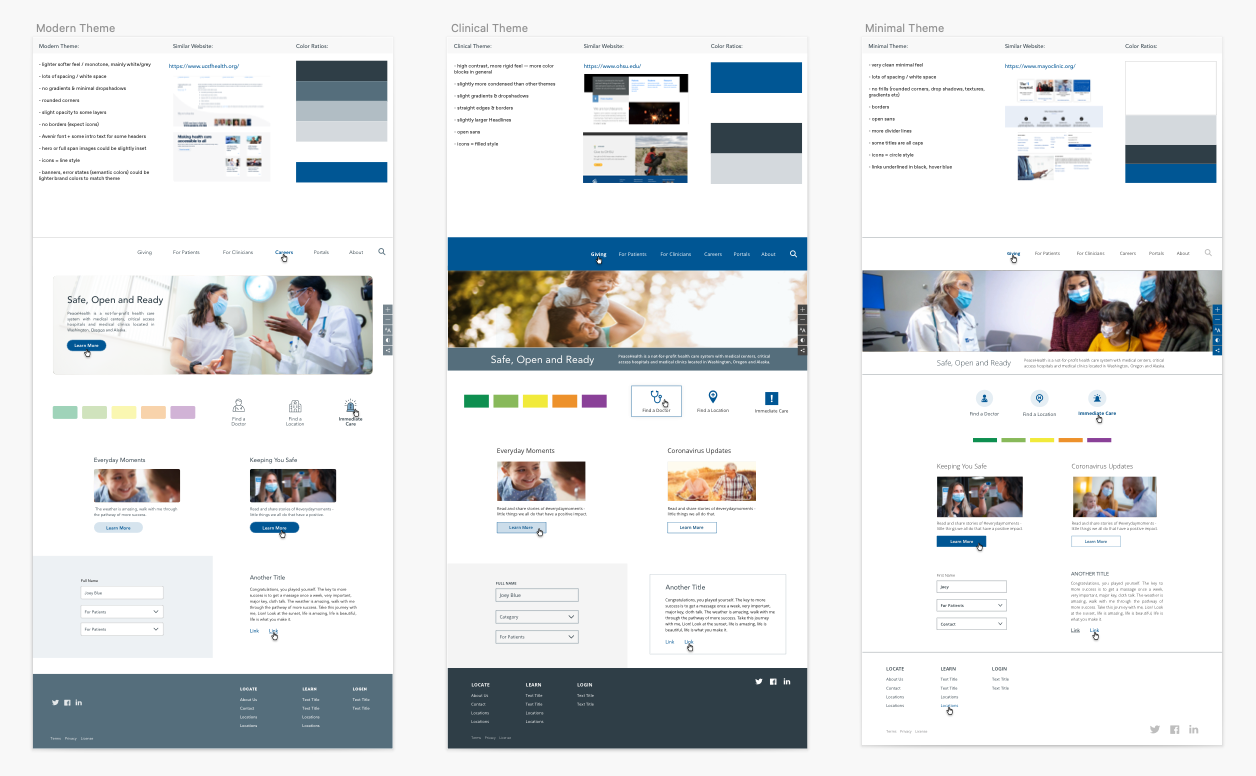
On the other hand, User Experience (UX) encompasses the entire journey a user takes with a product, from their initial awareness to ongoing sales engagement and loyalty. It goes beyond the visual elements and considers factors such as usability, accessibility, performance, and emotional resonance. UX design aims to create products that meet users’ needs, solve their problems, and provide a positive and memorable experience.
While UI focuses on the look and feel of a product through tools such as design systems, UX emphasizes the overall experience and satisfaction of the user. A well-designed UI is an essential component of a good UX, but it is not the only factor. UX design takes a holistic approach, considering the user’s context, motivations, and goals, and creating solutions that align with those needs.
Here are some key differences between UI and UX:
- Scope: UI focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a product, while UX encompasses the entire user journey and experience.
- Goal: UI aims to create an attractive and intuitive interface, while UX seeks to create a meaningful and valuable experience for the user.
- Focus: UI emphasizes the product’s look and feel, while UX prioritizes the user’s needs, behaviors, and emotions.
- Skills: UI design requires skills in visual design, typography, and interaction design, while UX design involves user research, information architecture, and usability testing.
Despite their differences, UI and UX are highly interdependent and work together to create a seamless and engaging user experience. A beautiful and intuitive UI can enhance the overall UX, while a well-designed UX can make even a simple UI feel enjoyable and satisfying.
The Benefits of Investing in UX
Investing in User Experience (UX) design is not just a matter of creating aesthetically pleasing interfaces or following design trends. It is a strategic business decision that can have a profound impact on the success and growth of an organization. By prioritizing UX, companies can reap numerous benefits that go beyond user satisfaction and extend to the bottom line. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of investing in UX.
1. Increased User Satisfaction and Loyalty
One of the primary goals of UX design is to create products that meet users’ needs and exceed their expectations. By providing a seamless, intuitive, and enjoyable user experience, companies can boost user satisfaction and foster a sense of loyalty. Satisfied users are more likely to return to the product, recommend it to others, and develop a positive emotional connection with the brand. In a competitive market, user loyalty can be a significant differentiator and a key driver of long-term success.
2. Higher Conversion Rates and Revenue
A well-designed user experience can directly impact a company’s bottom line by increasing conversion rates and revenue. When users can easily navigate a website or app, find what they need, and complete their desired actions, they are more likely to make a purchase, subscribe to a service, or engage with the brand in other meaningful ways.
Conversely, a poor user experience can lead to high bounce rates, abandoned shopping carts, and lost revenue opportunities. By optimizing the user journey and removing barriers to conversion, UX design can help companies maximize their revenue potential.
3. Reduced Development Costs and Time to Market
Investing in UX design early in the product development process can actually save companies time and money in the long run. By conducting user research, creating prototypes, and testing designs iteratively, UX designers can identify and address usability issues before the product is built, reducing the need for costly redesigns and development rework.
A well-designed product is also easier to develop, as it provides clear specifications and reduces the likelihood of scope creep or feature bloat. By streamlining the development process and minimizing unnecessary features, UX design can help companies bring products to market faster and more efficiently.
4. Enhanced Brand Reputation and Differentiation
A great user experience can be a powerful brand differentiator. Companies that consistently deliver exceptional UX across their products and services can establish a reputation for customer-centricity, innovation, and quality. A strong UX design can also help companies stand out from competitors and attract users who value seamless and delightful experiences. By investing in UX, companies can cultivate a positive brand image that resonates with users and sets them apart in the market.
5. Improved User Adoption and Retention
A well-designed user experience can significantly improve user adoption and retention rates. When users can quickly understand and navigate a product, they are more likely to adopt it into their daily routines and workflows. A great UX can keep users engaged and coming back to the product over time, reducing churn and increasing lifetime value. By designing products that are not only useful but also enjoyable and habit-forming, companies can build a loyal user base that drives sustainable growth.
6. Reduced Support Costs and Customer Complaints
Investing in UX design can also help companies reduce support costs and customer complaints. When products are intuitive and easy to use, users are less likely to encounter issues or require assistance. Clear navigation, helpful error messages, and accessible support resources can empower users to self-serve and resolve problems independently. By minimizing user frustration and reducing the need for customer support, UX design can help companies save time and resources while improving customer satisfaction.
The benefits of investing in UX are clear and compelling. By prioritizing user needs, designing for usability and engagement, and continually iterating based on feedback and data, companies can create products that not only delight users but also drive business success. As digital experiences become increasingly central to our lives, the value of UX will only continue to grow, making it a critical investment for any organization that wants to thrive in the digital age.
User Experience: The Heart of Successful Digital Product Strategy
User Experience (UX) has emerged as a critical factor in the success of any product or service. As users increasingly expect seamless, intuitive, and enjoyable experiences across all touchpoints, companies that prioritize UX are well-positioned to stand out, attract loyal customers, and drive long-term growth.
Throughout this guide, we have explored the fundamental concepts, principles, and best practices of UX design. We have seen how UX encompasses all aspects of a user’s interaction with a product, from their initial awareness to their ongoing engagement and loyalty. By understanding the difference between UX and UI, the five elements of UX, and the iterative design process, designers and businesses can create products that truly resonate with users.
Creating an exceptional user experience requires a deep understanding of users’ needs, behaviors, and preferences. It demands a commitment to research, testing, and continuous improvement, as well as a willingness to put the user at the center of every design decision. By following best practices such as designing for usability, consistency, and emotional engagement, companies can create products that not only meet functional requirements but also delight and inspire users.
The benefits of investing in UX are numerous and far-reaching. From increased user satisfaction and loyalty to higher conversion rates and revenue, a great UX can have a profound impact on a company’s bottom line. By reducing development costs, improving user adoption and retention, and enhancing brand reputation, UX design can help organizations achieve sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
As we look to the future, the importance of UX will only continue to grow. With the proliferation of digital devices, platforms, and services, users will demand ever-more seamless and personalized experiences. Companies that embrace UX as a core competency and a strategic priority will be best positioned to meet these evolving user needs and expectations.
Whether you are a designer, developer, product manager, or business leader, understanding and prioritizing UX is essential for success in the digital age. By putting users first, designing with empathy and purpose, and continually striving for improvement, you can create products that not only solve problems but also enrich people’s lives.
So, as you embark on your own UX journey, remember the key lessons and insights from this guide. Embrace the power of user-centered design, collaborate with cross-functional teams, and always keep the user at the heart of your work. By doing so, you can create meaningful, memorable, and impactful experiences that set your products and your business apart.